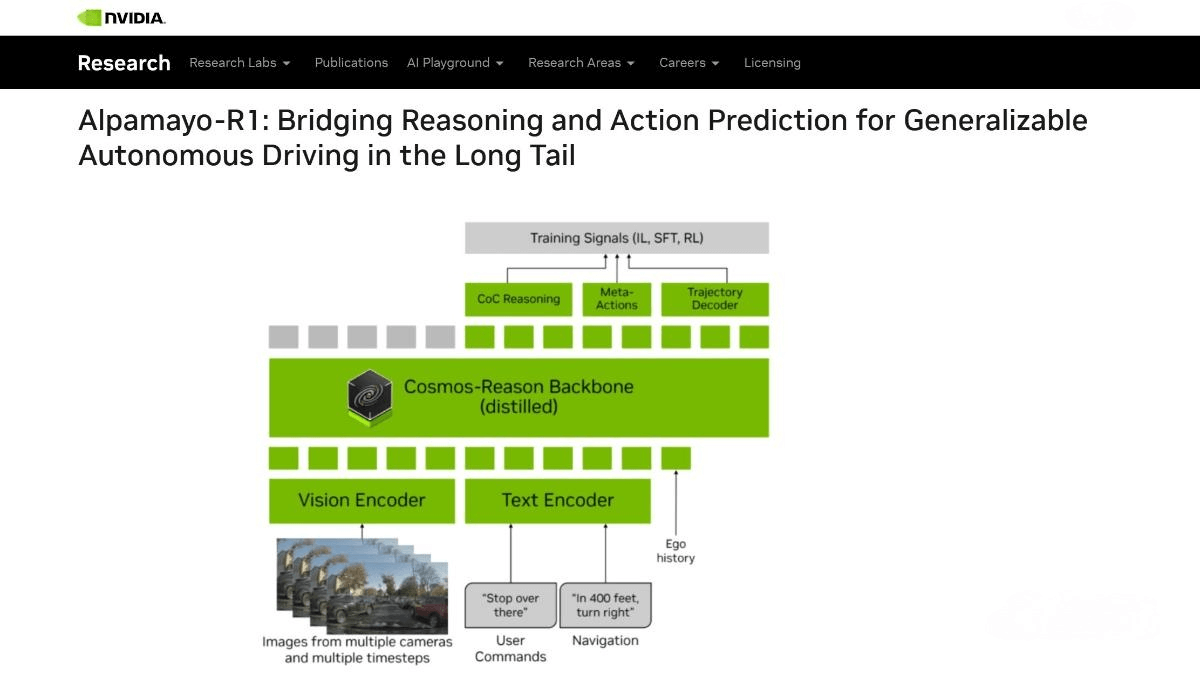
Alpamayo-R1 — NVIDIA’s inference-version Vision-Language-Action model
What is Alpamayo-R1?
Alpamayo-R1 (AR1) is a Vision–Language–Action (VLA) model released by NVIDIA that enhances autonomous-driving decision-making and generalization through causal reasoning. Its core innovations include: building a Causal-Chain (CoC) dataset generated via a “human–AI collaboration + automatic annotation” workflow to produce high-quality reasoning trajectories; adopting Cosmos-Reason as the VLM backbone—trained on large-scale visual-question-answering data to gain physical commonsense and embodied reasoning capabilities; and introducing a multi-stage training strategy that combines supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning to improve reasoning quality and trajectory generation.
In experiments, AR1 significantly improves planning accuracy, reduces off-road and near-collision rates, and maintains 99 ms end-to-end latency—making it suitable for real-time autonomous-driving applications.
Key Features of Alpamayo-R1
Causal reasoning and trajectory planning:
Through the Causal-Chain (CoC) dataset, AR1 performs causal reasoning and generates decision-aligned trajectories, improving accuracy and generalization in driving decisions.
Efficient visual encoding and feature extraction:
The optimized visual encoder improves multi-camera feature extraction efficiency by 10–20×, significantly reducing computational cost.
Real-time performance and low latency:
End-to-end inference takes only 99 ms, meeting the strict real-time requirements of autonomous driving.
Improved trajectory quality:
In both open-loop and closed-loop evaluations, AR1 significantly reduces off-route and near-collision rates, generating smoother and safer trajectories.
Open source to accelerate industry progress:
As an open-source model, AR1 lowers the barrier for autonomous-driving R&D and provides strong support for automakers and research institutions.
Technical Principles of Alpamayo-R1
Causal-Chain (CoC) dataset:
Constructed via a hybrid workflow of automated annotation and human-AI collaboration, the dataset contains decision-aligned reasoning trajectories with explicit causal relationships. It consists of three structured components: driving decisions, causal factors, and combined CoC trajectories.
Modular VLA architecture:
Integrates the Cosmos-Reason vision-language model—pre-trained for physical-intelligence applications—and a diffusion-based trajectory decoder capable of generating dynamic and drivable paths in real time.
Multi-stage training strategy:
Supervised fine-tuning activates the model’s reasoning capabilities, while reinforcement learning enhances reasoning quality through feedback from large-scale reasoning models, ensuring consistency between reasoning and actions.
Efficient visual encoding:
Supports high-efficiency multi-camera tokenizers such as the triplane tokenizer and Flex tokenizer, drastically reducing token count to meet real-time inference requirements.
Action expert trajectory decoder:
Built on a flow-matching framework, it efficiently generates continuous, multi-modal trajectory plans aligned with language-reasoning outputs while maintaining real-time performance.
Project Links
Official website: https://research.nvidia.com/publication/2025-10_alpamayo-r1
arXiv paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2511.00088v1
Application Scenarios of Alpamayo-R1
Autonomous-driving decision-making and planning:
AR1 generates safe and efficient driving trajectories through causal reasoning, making it suitable for complex traffic environments and improving vehicle autonomy.
Traffic scenario simulation and testing:
Useful for building virtual driving environments and simulating diverse traffic situations to evaluate the performance and safety of autonomous-driving systems.
Intelligent transportation optimization:
Provides decision-support for intelligent traffic systems, helping optimize traffic flow, reduce congestion, and improve overall efficiency.
Vehicle safety and obstacle avoidance:
Real-time trajectory planning and obstacle-avoidance capabilities help reduce accident risk and improve vehicle safety in complex surroundings.
Related Posts