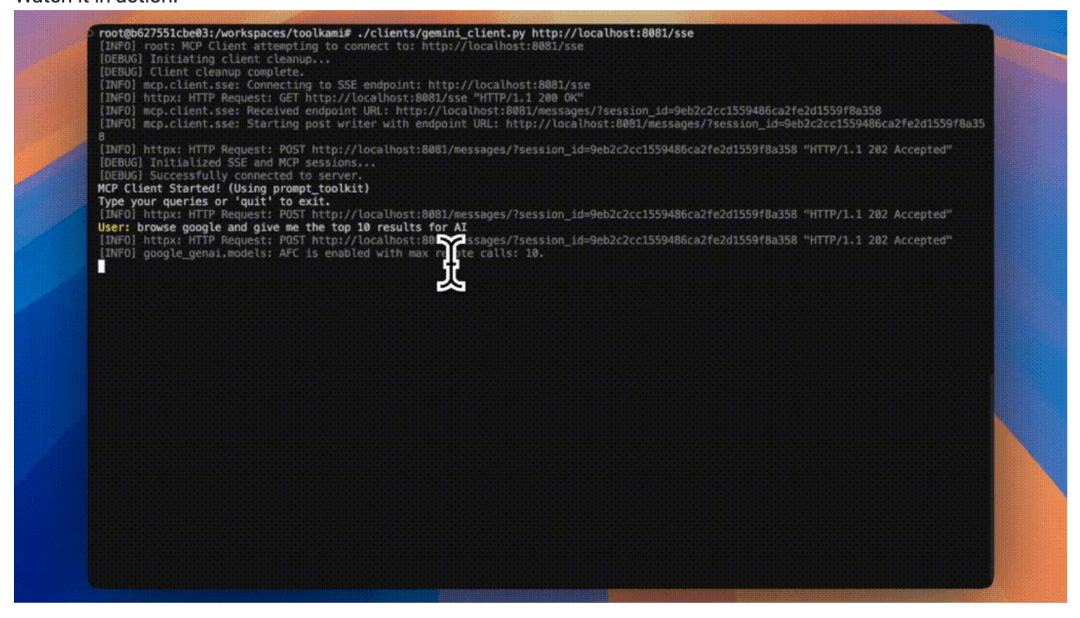
What is CoF?
CoF (Chain-of-Frames) is a new concept introduced by DeepMind, analogous to the “Chain-of-Thought” (CoT) in language models. CoF enables video models to reason across time and space by generating videos frame by frame to solve complex visual tasks. For example, the Veo 3 model uses CoF to solve maze problems, complete symmetry tasks, or perform simple visual analogical reasoning. Just as language models solve problems through symbolic reasoning, CoF achieves visual reasoning by generating coherent video frames, demonstrating the potential of video models for general visual understanding.

Key Features of CoF
-
Visual Reasoning: By generating videos frame by frame, CoF can solve problems step by step, such as finding a path through a maze, completing symmetry tasks, or conducting visual analogy reasoning.
-
Spatiotemporal Operations: Enables manipulation of objects in videos—such as moving, deforming, or changing attributes—while maintaining coherence.
-
General Visual Understanding: Helps video models grasp physical rules, abstract relationships, and dynamic changes in the visual world, enabling zero-shot learning for general visual tasks.
-
Coherent Video Generation: Ensures that generated videos are temporally and spatially coherent, producing outputs that align with logical and physical constraints.
Technical Principles of CoF
-
Generative Models: CoF relies on large-scale generative models trained on massive datasets to learn the spatiotemporal structures and dynamics of videos.
-
Prompt-Driven: Natural language prompts and initial images guide the model to generate videos aligned with task requirements. Prompts define task goals, while the initial image provides the first frame.
-
Frame-by-Frame Reasoning: The model generates each frame based on the previous one and the prompt, mirroring the stepwise reasoning process of CoT in language models.
-
Physical and Logical Constraints: Generated videos must follow physical laws and logical consistency. For example, objects must move according to physics, and elements in the video cannot break real-world constraints.
-
Optimization and Feedback: Through multiple attempts and refinements, the model improves accuracy—for example, generating multiple outputs and selecting the best result increases task success rates.
Project Link
- Technical paper: https://papers-pdfs.assets.alphaxiv.org/2509.20328v1.pdf
Application Scenarios of CoF
-
Maze Solving: CoF can generate videos showing how an object finds the optimal path from start to finish in a maze, planning the route step by step.
-
Visual Symmetry Tasks: CoF can generate symmetric patterns or images, filling in missing parts frame by frame to complete symmetric figures.
-
Physics Simulation: Simulates physical phenomena such as motion, collisions, or buoyancy, producing videos that comply with the laws of physics.
-
Image Editing: Applied in tasks like background removal, style transfer, or colorization, progressively completing edits through frame-by-frame video generation.
-
Visual Analogy: Solves visual analogy problems by generating missing parts to complete an analogy, reasoning frame by frame to reach the correct solution.
Related Posts