MiDashengLM – Xiaomi’s Open-Source Efficient Audio Understanding Large Model
What is MiDashengLM?
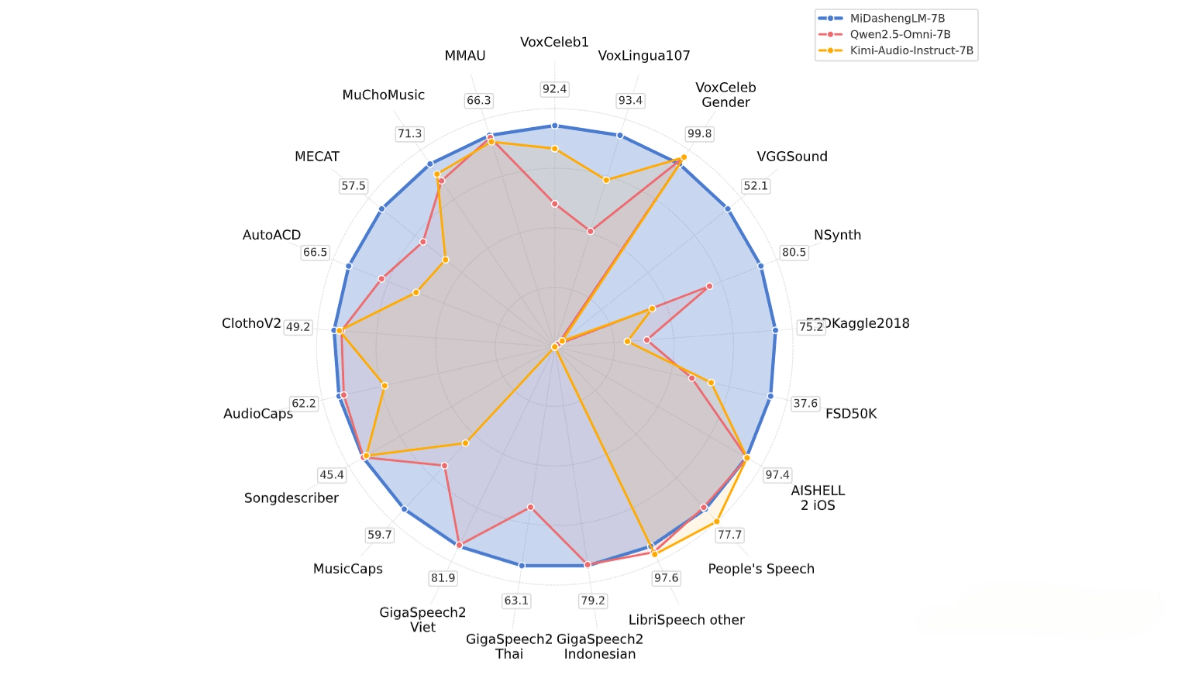
MiDashengLM is Xiaomi’s open-source, high-efficiency large model for audio understanding, specifically the MiDashengLM-7B version. Built on the Xiaomi Dasheng audio encoder and the Qwen2.5-Omni-7B Thinker decoder, the model uses a unified audio captioning alignment strategy to achieve comprehensive understanding of speech, environmental sounds, and music. It features exceptional performance and high inference efficiency, with first-token latency only a quarter of that in leading models. It also supports large-scale parallel processing. All training data is fully open-source and available for both academic and commercial use. The model is well-suited for applications such as smart cockpits and smart homes, advancing multimodal interaction experiences.
Key Features of MiDashengLM
-
Audio Captioning:
Converts audio input—including speech, environmental sounds, and music—into natural language descriptions, helping users quickly grasp audio content. -
Audio Classification:
Identifies specific audio categories (e.g., speech, environmental sound, music), useful in scenarios like sound recognition and music classification. -
Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR):
Transcribes spoken language into text, supporting multiple languages and widely applied in voice assistants and in-vehicle systems. -
Audio Question Answering:
Answers questions based on input audio content. Applicable in smart cockpit scenarios for understanding ambient sound or music-related queries. -
Multimodal Interaction:
Combines audio with other modalities (such as text or images) for integrated understanding, enhancing interactive experiences on smart devices.
Technical Overview of MiDashengLM
Model Architecture
-
Audio Encoder:
Based on the Xiaomi Dasheng encoder, which transforms raw audio signals into high-dimensional representations. It excels in understanding non-speech audio like environmental sounds and music, capturing rich semantic information. -
Decoder:
Built on the Qwen2.5-Omni-7B Thinker, an autoregressive decoder that converts encoded features into natural language. The decoder supports various tasks including audio captioning, audio QA, and ASR.
Training Strategy
-
Unified Audio Caption Alignment:
Avoids the limitations of traditional ASR transcription by using non-monotonic global semantic mapping. This forces the model to learn deep semantic associations within audio scenes, achieving unified understanding of speech, environmental sound, and music. -
Multi-Expert Annotation Pipeline:
Training data is generated using a pipeline of expert models with fine-grained labels across speech, vocals, music, and acoustic environments. Final descriptions are synthesized using the DeepSeek-R1 reasoning model. -
Datasets:
Trained on publicly available datasets spanning speech, environmental sound, and music, totaling over 1 million hours. Original labels are discarded during pretraining, replaced with rich textual descriptions to compel the model to learn comprehensive audio semantics.
Inference Optimization
-
Efficient Inference:
By optimizing the encoder design, the output frame rate is reduced from Qwen2.5-Omni’s 25Hz to 5Hz, significantly lowering computational load and improving inference speed. -
Massive Parallel Processing:
Supports large batch sizes (batch size = 512). When processing 30 seconds of audio and generating 100 tokens on an 80GB GPU, MiDashengLM achieves over 20× the throughput of Qwen2.5-Omni-7B.
Project Links
-
GitHub Repository:
https://github.com/xiaomi-research/dasheng-lm -
HuggingFace Model Page:
https://huggingface.co/mispeech/midashenglm-7b -
Technical Report:
MiDashengLM Technical Paper (PDF) -
Online Demo:
https://huggingface.co/spaces/mispeech/MiDashengLM-7B
Application Scenarios of MiDashengLM
-
Smart Cockpits:
Improve driving safety and interaction through voice assistants and environmental sound recognition. -
Smart Homes:
Enable voice control and environmental audio monitoring for seamless home automation. -
Voice Assistants:
Offer multilingual speech recognition and intelligent dialogue capabilities to meet diverse user needs. -
Audio Content Creation and Tagging:
Automatically generate audio captions and metadata to streamline creative workflows. -
Education and Learning:
Assist in language and music education by providing pronunciation feedback and theoretical guidance.
Related Posts