GPT-5-Codex – an agent-optimized programming model launched by OpenAI
What is GPT-5-Codex?
GPT-5-Codex is a model launched by OpenAI, optimized specifically for programming and further enhanced on top of GPT-5. The model focuses on real-world software engineering tasks such as building projects from scratch, code refactoring, debugging, testing, and code review. It dynamically adjusts reasoning time based on task complexity—providing instant responses for simple tasks and deep reasoning for complex ones—and can independently handle complex tasks for up to 7 hours. Its code review ability is outstanding, capable of accurately identifying critical defects while reducing redundant comments. GPT-5-Codex also supports multimodal input, enabling cloud-based image or screenshot processing and progress visualization, making it a powerful programming assistant for developers.
Key Features
-
Code generation & optimization: Quickly generates high-quality code from natural language descriptions, supports multiple programming languages, and optimizes existing code for better performance.
-
Code review: Automatically identifies critical defects and potential issues in code, generating detailed review reports to help developers quickly locate and fix problems.
-
Interactive programming: Provides rapid responses to simple tasks in interactive sessions, while also being capable of independently handling complex tasks such as large-scale refactoring, working continuously for over 7 hours.
-
Multimodal input: Accepts images for frontend design and UI tasks, and provides intuitive feedback by displaying progress screenshots.
-
Integration & extension: Seamlessly integrates into VS Code, GitHub, ChatGPT, and other development environments, while supporting external tool calls such as web search to improve development efficiency.
Performance of GPT-5-Codex
-
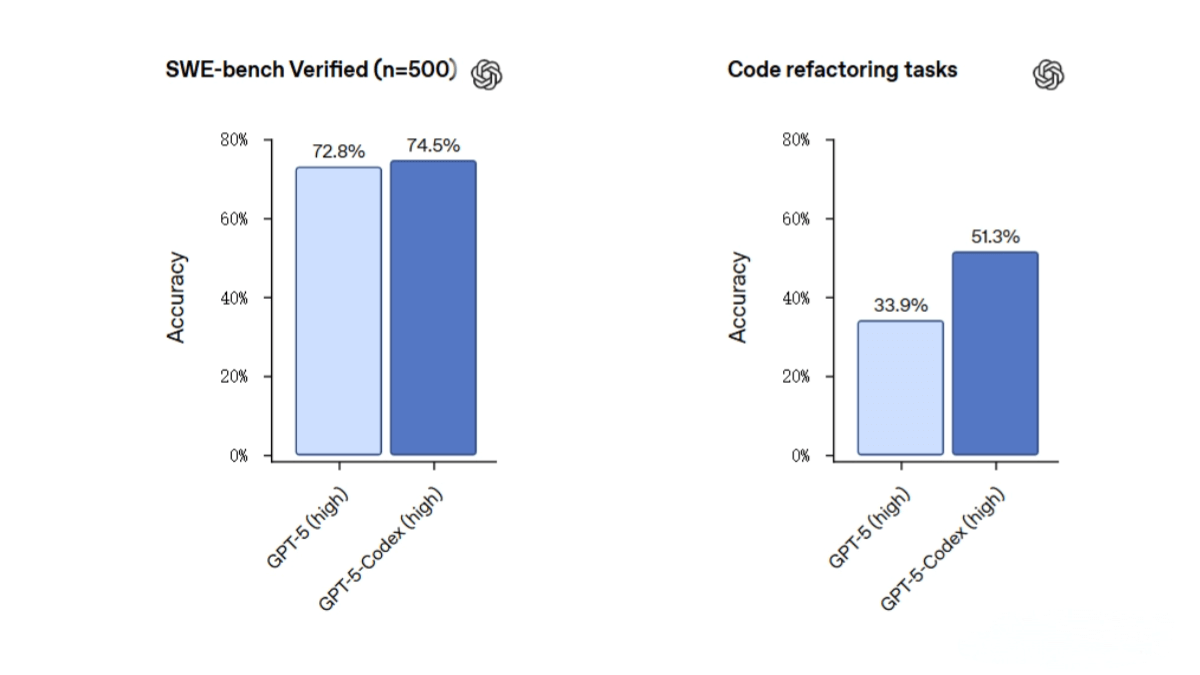
Code generation & optimization: Achieves 74.5% accuracy on the SWE-bench Verified benchmark, higher than GPT-5’s 72.8%. In code refactoring tasks, accuracy improves from GPT-5’s 33.9% to 51.3%.
-
Dynamic reasoning time: Adjusts computational resources based on task complexity. For simple tasks, token usage is reduced by 93.7% compared to GPT-5, while for complex tasks token usage increases by 102.2%. It can independently work for over 7 hours on large, complex tasks.
-
Code review ability: Maintains an error comment rate of just 4.4% (vs. GPT-5’s 13.7%), with high-impact comments accounting for 52.4% (vs. GPT-5’s 39.4%). The average number of comments per PR is reduced from 1.32 (GPT-5) to 0.93, effectively identifying critical defects and reducing unnecessary feedback.
-
Multimodal handling: Supports image inputs for frontend design and UI tasks, provides progress screenshots, and improves development experience.
-
Integration & extension: Integrates with VS Code, GitHub, ChatGPT, and more. With container caching technology, the median completion time for both new and follow-up tasks is reduced by 90%, boosting efficiency.
Core Advantages of GPT-5-Codex
-
Optimization focus: As a specialized version of GPT-5, GPT-5-Codex is optimized for agent-based coding in Codex, with training focused on real-world software engineering tasks, including building projects from scratch, adding features and tests, debugging, executing large-scale refactoring, and conducting code reviews.
-
Dynamic reasoning time: Automatically decides how much computational resource to invest based on task complexity. For the simplest 10% of tasks, token usage is reduced by 93.7% compared to GPT-5; for the most complex 10% of tasks, it doubles reasoning, editing, testing, and iteration time, enabling over 7 hours of autonomous work.
-
Code review ability: Specially trained for code review and defect detection, capable of navigating codebases, reasoning through dependencies, running code, and executing tests to verify correctness. Evaluations show only a 4.4% error comment rate (vs. GPT-5’s 13.7%), with 52.4% high-impact comments (vs. GPT-5’s 39.4%), and an average of just 0.93 comments per PR (vs. GPT-5’s 1.32).
-
Frontend performance: Demonstrates significant improvement in human preference assessments for building mobile websites. In cloud-based workflows, it supports reviewing user-provided images or screenshots, visually checking progress, and presenting work snapshots to users.
Limitations of GPT-5-Codex
-
Task selectiveness: Places certain restrictions on task scope and feasibility, and may reject overly complex tasks outright.
-
Environment setup issues: During setup, it may make incorrect assumptions about a user’s development environment, requiring manual reconfiguration of system files and settings, which adds preparation overhead.
-
Multi-agent workflow limitations: While it understands the concept of multiple agents, it does not implement true sub-agents, and unlike Claude Code, cannot automatically continue long-term research tasks.
Project Information
- Official site: https://openai.com/index/introducing-upgrades-to-codex/
Application Scenarios of GPT-5-Codex
-
Full-cycle software development: From building complete projects from scratch—including code implementation after requirements analysis, feature additions, test writing, debugging, and large-scale refactoring.
-
Code review stage: Automatically reviewing code before deployment, identifying critical vulnerabilities and potential issues, and helping teams improve code quality and development efficiency.
-
Interactive programming collaboration: Working with developers in interactive sessions for quick responses to simple tasks, while independently managing complex, long-duration tasks such as large-scale refactoring.
-
Frontend design & development: Supports image inputs for frontend and UI tasks, interprets user-provided design diagrams or screenshots, generates corresponding code, and displays progress snapshots.
Related Posts