Fara-7B – Microsoft’s Open-Source Small-Scale Agentic Computer Model
What is Fara-7B?
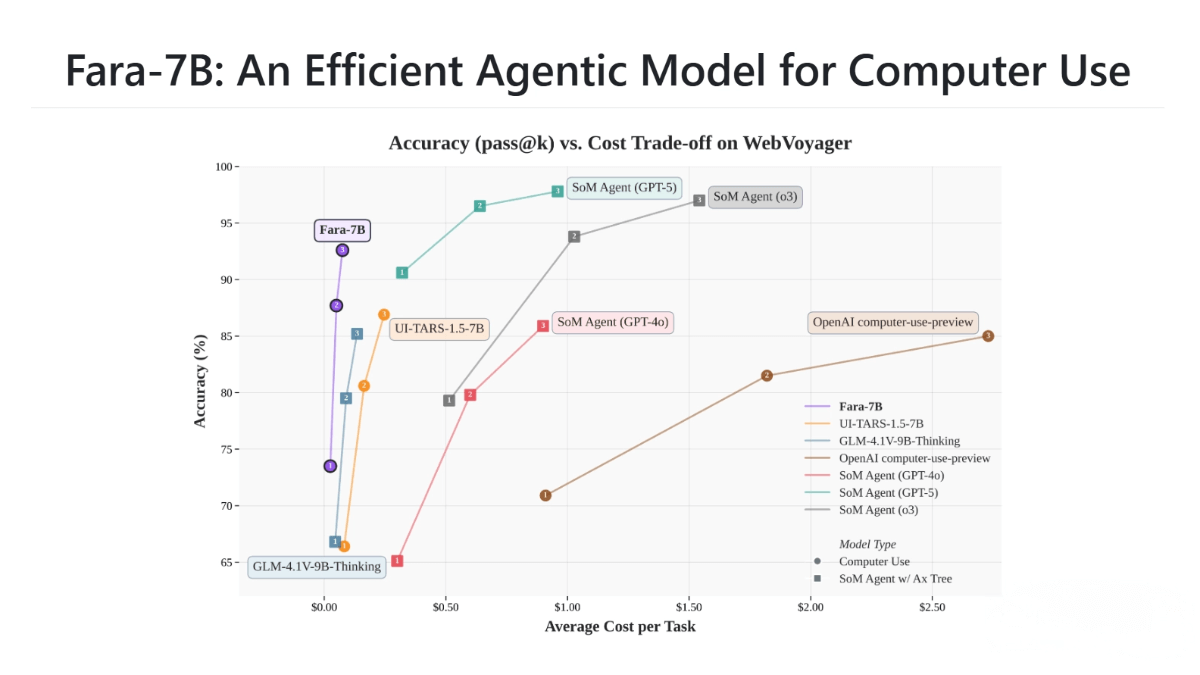
Fara-7B is Microsoft’s open-source, agentic Small Language Model (SLM) designed specifically for computer-use tasks. The model perceives webpages visually and operates interface elements such as the mouse and keyboard to help users complete tasks like filling forms, searching for information, or booking travel.With only 7 billion parameters, it delivers top-tier performance in its size class and can run directly on local devices, reducing latency and improving privacy.Fara-7B is trained with synthetic data, enabling efficient task execution while emphasizing safety. It is currently released as an experimental version to invite community exploration and feedback, driving ongoing technological progress.
Key Features
1. Automated task execution
Operates mouse, keyboard, and other UI elements to help users accomplish various computer tasks such as form filling, information search, travel booking, and account management.
2. Visual perception and interaction
The model directly perceives webpage content and performs actions—clicking, scrolling, typing—by predicting coordinates. It operates solely based on screen visuals without requiring auxiliary information (e.g., accessibility trees).
3. User interaction and control
During task execution, Fara-7B pauses at critical moments—such as when encountering sensitive information or important decisions—to wait for user confirmation or additional input, ensuring full user control.
4. Privacy protection and safety
All operations are executed locally on the device, ensuring no user data is transmitted externally. Actions are run within a sandboxed environment and fully logged for auditability.
5. Efficient task execution
Thanks to an optimized architecture and training pipeline, Fara-7B completes tasks in fewer steps—making it more efficient and cost-effective than other models of similar size.
Technical Principles of Fara-7B
► Vision-based interaction
The model perceives webpages through screenshots and simulates human-computer interaction directly, without relying on internal webpage structures such as the DOM or accessibility tree.
► Synthetic data generation
To overcome the shortage of high-quality training data, Microsoft built a synthetic data pipeline that generates large-scale, multi-step task data from public webpages and task prompts—avoiding the high cost of manual annotation.
► Multi-agent system for training
During training, a multi-agent system solves synthetic tasks to generate demonstration data for supervised fine-tuning. This system includes a task planner, webpage operator, and user simulator, which work together to complete tasks.
► Single-model distillation
The complexity of the multi-agent system is distilled into a single model, allowing Fara-7B to operate independently and making deployment lightweight and simple.
► Enhanced safety mechanisms
Safety data is incorporated during training, enabling the model to refuse harmful requests. All actions are logged to ensure full user oversight and accountability.
Project Links
-
Project homepage: microsoft.com/en-us/research/blog/fara-7b-an-efficient-agentic-model-for-computer-use/
-
GitHub repository: github.com/microsoft/fara
-
HuggingFace model page: huggingface.co/microsoft/Fara-7B
-
Technical paper: microsoft.com/en-us/research/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/Fara-7B-An-Efficient-Agentic-Model-for-Computer-Use.pdf
Application Scenarios of Fara-7B
• Office automation:
Automatically processes documents, writes emails, and performs data entry to significantly improve productivity.
• Information retrieval and organization:
Quickly searches the web and summarizes information to help users efficiently gather needed materials.
• E-commerce:
Searches for products, compares prices, and assists with purchasing, optimizing the shopping experience.
• Travel planning:
Intelligently arranges itineraries and books flights and hotels, simplifying the preparation process.
• Online learning:
Searches for courses, organizes learning materials, and helps users learn efficiently.
Related Posts