Oliva – Open-source Speech RAG Assistant, Real-time Speech Search Vector Database
What is Oliva?
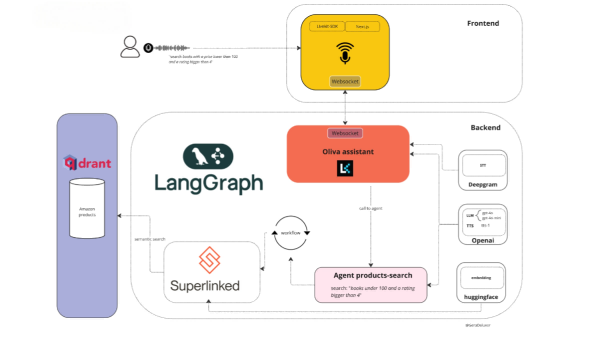
Oliva is an open-source voice-driven RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) assistant that integrates Langchain and Superlinked technologies. Built on a voice-driven RAG architecture, it enables users to search for information in real-time within the Qdrant vector database. Users can ask questions in natural language, and Oliva utilizes speech-to-text and real-time voice communication technologies to convert voice commands into database queries, returning structured results. Oliva supports multi-agent collaboration, breaking down complex questions into multiple subtasks and assigning them to different agents for processing.
The main functions of Oliva
- Real-time Voice Search: Users ask questions via voice, and AI responds in real time.
- Multi-agent Collaboration: Decomposes complex problems into multiple sub-tasks, with different agents handling them separately.
- Semantic Search: Utilizes the Qdrant vector database to understand semantics and provide accurate search results.
- Flexible Integration: Supports importing local documents, API data sources, online web pages, etc., as knowledge bases.
The technical principle of Oliva
- Speech Recognition and Synthesis: Leveraging Deepgram’s speech-to-text service, users’ voice commands are converted into text for further processing. System-generated text responses are converted into voice output and provided to users.
- Vector Database: Utilizing the Qdrant vector database for data storage and retrieval. Qdrant is an efficient vector database capable of quickly handling similarity searches for vector embeddings and supporting semantic search functionality.
- Langchain Multi-Agent Architecture: Building a multi-agent system based on the Langchain framework. Each agent is responsible for specific tasks, such as retrieval, generating responses, or executing operations. Through dynamic task routing, agents collaborate to fulfill complex query requirements.
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): The RAG architecture combines retrieval and generation techniques. The retrieval module fetches relevant information from the vector database, while the generation module integrates the retrieved information into natural language responses.
- Real-time Communication: Integrated with the Livekit real-time communication platform to support real-time voice interaction. Users interact with Olivia through voice, and the system processes voice commands in real time and returns voice responses.
- Semantic Understanding: Based on Natural Language Processing (NLP) technology, the system understands users’ natural language instructions. By using vector embedding techniques, users’ voice commands are converted into vectors and compared for similarity with vectors in the database, providing accurate search results.
The project address of Oliva
- GitHub Repository: https://github.com/Deluxer/oliva
Application scenarios of Oliva
- Enterprise Knowledge Library Search: Enterprise employees can use voice commands to quickly query internal documents, technical manuals, FAQs and other knowledge library content, improving work efficiency.
- Intelligent Customer Service Assistant: As the voice interaction front-end of the customer service system, it helps customers quickly solve common problems and provides 24/7 uninterrupted voice support.
- Smart Home Control: Use voice commands to control smart home devices, such as lighting, temperature adjustment, appliance switching, etc., enhancing the intelligent home experience.
- Data Analysis and Reporting: Users obtain data analysis results through voice questions, such as querying sales data, market trends, etc., and the system provides feedback in voice form.
- Mobile Voice Assistant: Integrated into mobile devices as a personal voice assistant, it helps users search for information, set reminders, navigate, etc.
© Copyright Notice
The copyright of the article belongs to the author. Please do not reprint without permission.
Related Posts

No comments yet...