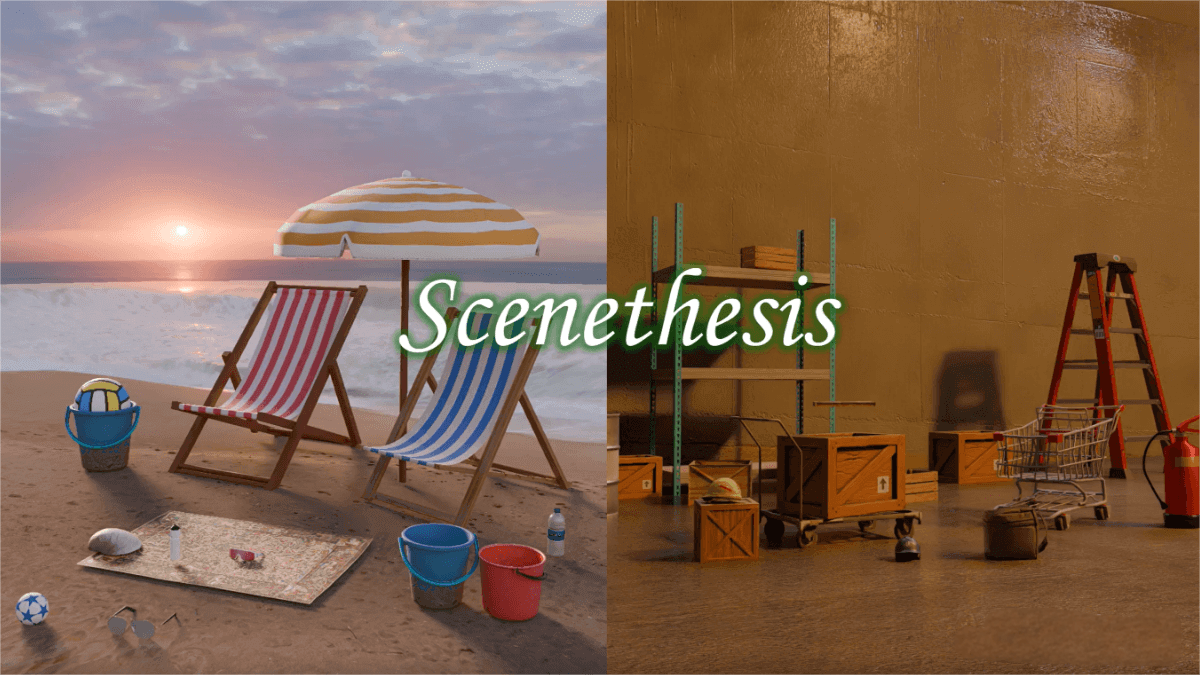
Scenethesis – an interactive 3D scene generation framework launched by NVIDIA
What is Scenethesis
Scenethesis is an innovative framework developed by NVIDIA for generating interactive 3D scenes from text descriptions. It integrates large language models (LLMs) with advanced visual perception technologies, following a multi-stage process for efficient scene generation. The framework uses LLMs for rough layout planning, visual modules to refine layouts with image guidance, optimization modules to adjust object poses for physical plausibility, and validation modules to ensure spatial coherence. Scenethesis can generate diverse indoor and outdoor scenes with high realism and physical consistency, making it widely applicable in virtual content creation, simulation environments, and embodied AI research.
Key Features of Scenethesis
-
Text-to-3D Scene Generation: Users input textual descriptions, and AI automatically generates corresponding 3D scenes.
-
Physical Plausibility: Generated objects do not penetrate each other, are stably placed, and conform to physical rules.
-
User Interaction: Users can adjust object positions, sizes, etc., with real-time scene updates.
-
Diverse Scene and Object Library: Supports a wide range of indoor and outdoor environments with a rich selection of 3D models.
-
Scene Validation: Automatically checks scene quality and regenerates or optimizes as needed to ensure high-quality output.
Technical Workflow of Scenethesis
-
Rough Layout Planning (LLM Module): After the user inputs a text description, the LLM parses it to understand the scene’s theme and key elements. It selects relevant objects from a predefined 3D model library and generates a rough layout plan, including detailed prompts about object placement and relationships, laying the groundwork for visual refinement.
-
Visual Refinement (Visual Module): Based on the LLM prompts, a visual module (e.g., a diffusion-based image generator) produces detailed images to guide scene layout. Pretrained vision foundation models (like Grounded-SAM and DepthPro) perform segmentation and depth estimation on these images to extract scene graphs, which include 3D bounding boxes and spatial relationships of objects. The system then retrieves 3D models matching the scene description.
-
Physical Optimization (Physics Optimization Module): Using semantic correspondence methods such as RoMa, the system aligns 3D object poses with the image guidance, ensuring consistent position, size, and orientation. Signed Distance Field (SDF) techniques detect collisions between objects and adjust their positions and sizes to avoid overlap.
-
Scene Validation (Validation Module): A pretrained language model evaluates the spatial coherence of the generated scene, verifying that object placements and relationships make logical sense. If the evaluation fails, the system triggers re-planning and optimization steps until a high-quality scene is achieved.
Project Links
-
Official Website: https://research.nvidia.com/labs/dir/scenethesis/
-
arXiv Paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2505.02836
Application Scenarios
-
Virtual Reality (VR)/Augmented Reality (AR): Create immersive virtual environments, such as virtual tours or exhibitions.
-
Game Development: Rapidly generate game levels and virtual worlds, improving development efficiency.
-
Embodied AI: Provide realistic virtual environments for training AI agents, such as household settings.
-
Virtual Content Creation: Generate scene prototypes for films, animations, or advertisements, accelerating the creative process.
-
Education and Training: Simulate labs or training environments for teaching and skill development.
Related Posts