Leadership Isn’t Magic! Harvard AI Cracks the Four Core Algorithms of Elite Commanders
The stronger the leadership ability, the better the ability to direct AI Agents! This research report from Harvard Kennedy School, titled “Measuring Human Leadership Skills with AI Agents,” introduces a method to evaluate human leadership using AI Agents, which may redefine our understanding of the essence of “soft skills.”Web link
1. The “functional skeleton” of leadership
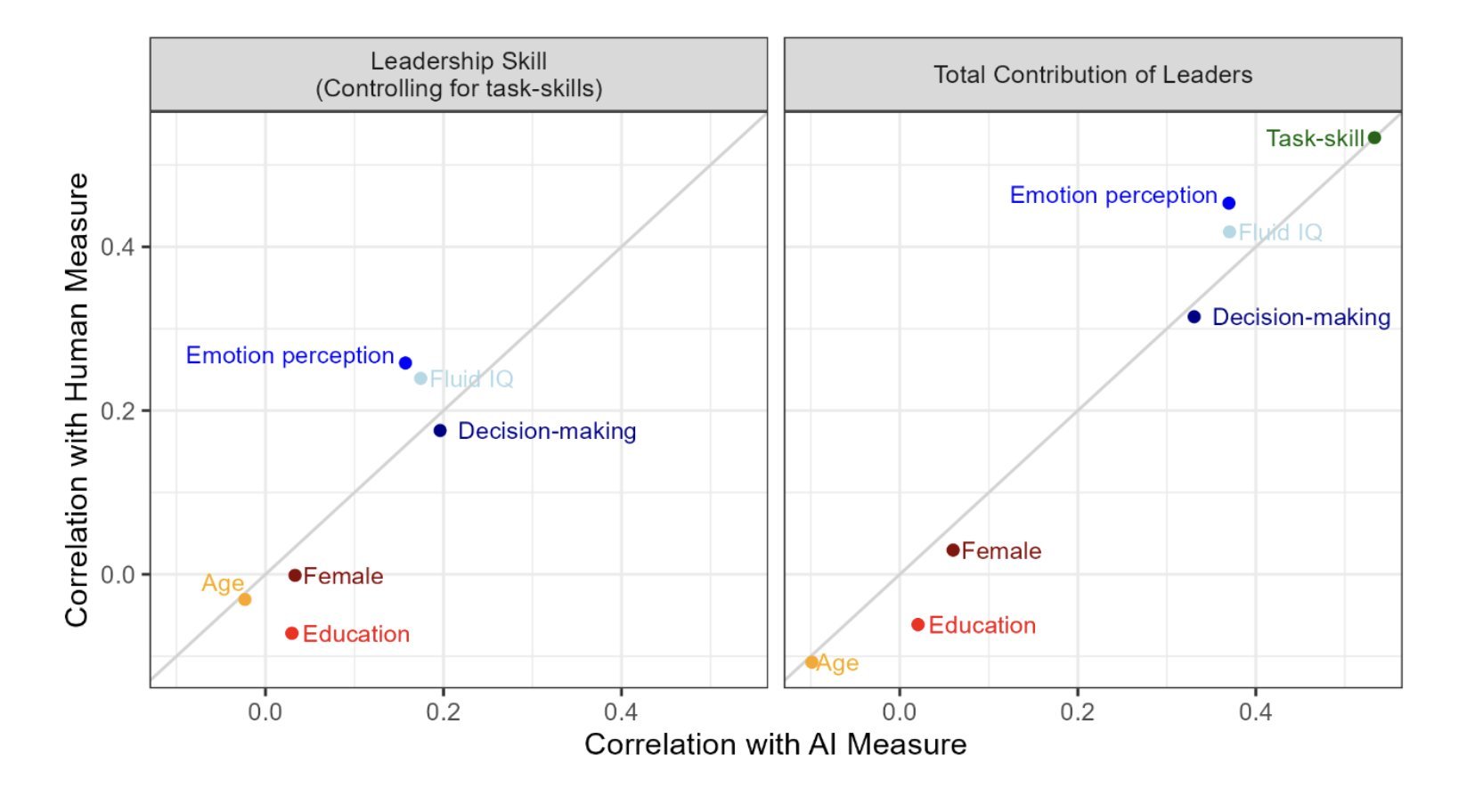
- This discovery suggests that, at least in goal-oriented and information-driven collaborative tasks, effective leadership may rely on a clearly definable “functional skeleton.” This skeleton is primarily composed of information processing, structured communication, task orientation, and decision-making logic.
- Although AI agents lack emotions or genuine understanding, they can produce predictable and logically consistent responses to structured information inputs and instructions. A leader who can effectively guide AI demonstrates their mastery of this “functional skeleton.” This ability is equally applicable to guiding human teams in handling similar structured tasks, as human teams also require clear instructions, effective information summarization, and a rational decision-making process.
Insight: This shows that beyond charm or interpersonal relationships, a key and measurable foundation of leadership lies in its ability to organize and process information flows to achieve goals. AI can precisely and effectively simulate and respond to this fundamental aspect.
2. Re-examining “Soft Skills”
- Traditionally, “soft skills” have been associated with deep interactions such as empathy, interpersonal communication, and emotional intelligence. However, this study reveals that observable behaviors such as “questioning techniques,” “facilitating conversational turn-taking,” and “using inclusive language” also demonstrate significant predictive value, even in interactions with non-human agents.
- This suggests that “soft skills” may encompass an important “procedural” or “behavioral pattern” dimension. These patterns (such as how to ask questions, how to structure conversations) inherently possess the function of enhancing collaboration efficiency. To some extent, their effectiveness can be independent of the interactors’ intrinsic emotional states or complex psychology. AI testing has successfully captured and measured the procedural value of these skills.
Insight: “Soft skills” are not entirely the “untransmittable” human magic. Their core may consist of behavioral strategies that are learnable, measurable, and possess a certain degree of universality across different interacting entities (humans or AIs).
3. The Boundaries of Emotion and the Limitations of AI
- The paper explicitly states that emotional factors (the leader’s positive emotions and the perception of followers’ emotions) have relatively weak predictive power in AI testing. This is precisely one of the most insightful findings, as it delineates the current boundaries of AI simulation capabilities.
- AI can simulate information processing and communication structures but struggles to replicate genuine human emotional interactions and their impact on team atmosphere, trust, and long-term motivation. This indicates that while AI testing is effective in measuring the cognitive and structural dimensions of leadership, it may underestimate the importance of the emotional dimension in more complex, long-term, or high-stakes interpersonal interactions.
Insight: Currently, AI can capture the “cold cognition” and “structured” aspects of leadership. However, the “hot cognition” and “emotional connection” aspects remain unique to human leadership and are areas that AI still struggles to fully replace.
This research not only concerns measuring humans with AI but also reveals the essence of effective human-AI collaboration. Those leaders who are good at constructing tasks, clarifying goals, and managing information flow can not only lead humans better but also make more effective use of AI as a team member or tool.
Note: In the figure, the task skills, decision-making abilities, and IQ of the characters are close to the diagonal line and concentrated in the upper right corner, indicating a high positive correlation between human leadership and AI testing 👀.
Related Posts