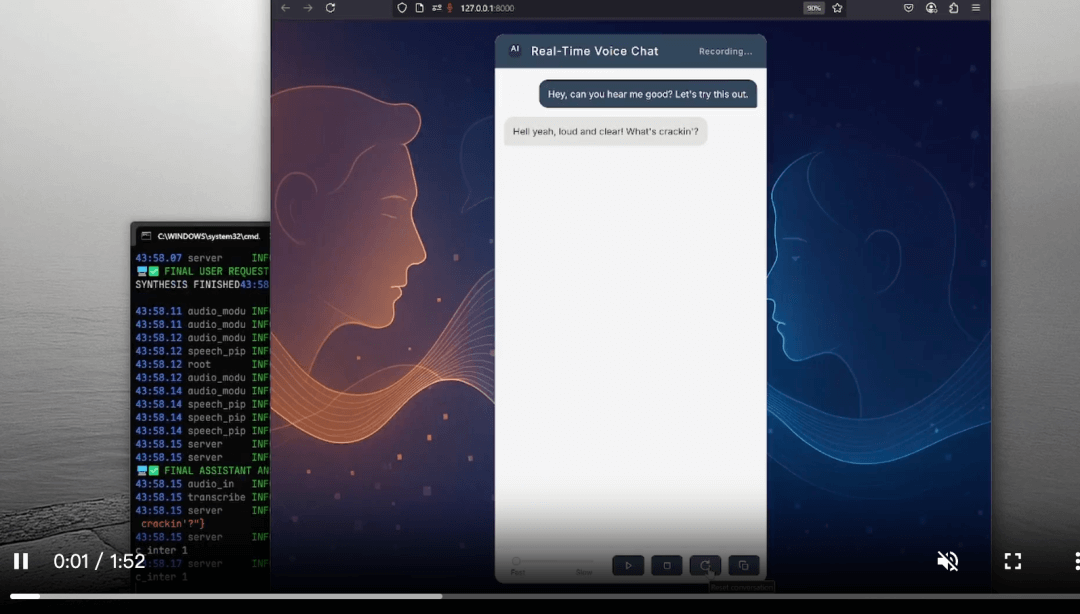
Talk to AI with Your Voice: Exploring the Real-Time Interaction Power of RealtimeVoiceChat
What is RealtimeVoiceChat?
RealtimeVoiceChat is an open-source project developed by KoljaB, designed to enable natural, real-time spoken conversations with AI. By integrating advanced speech-to-text (STT), text-to-speech (TTS), and large language models (LLMs), users can speak directly to an AI and receive voice responses instantly—creating a seamless, immersive communication experience.
Key Features
-
Natural Voice Conversations: Users can interact with AI entirely through voice—no keyboard required.
-
Low Latency Responses: Optimized audio streaming ensures minimal delay between user speech and AI response.
-
Web-Based Interface: Runs in the browser with no installation required, accessible anytime, anywhere.
-
Customizable Model Integration: Supports a variety of LLM backends (e.g., OpenAI GPT), giving users flexibility.
-
Open and Extensible: Fully open-source, making it easy for developers to build on and adapt for different use cases.
How It Works (Technical Overview)
The system uses a client-server architecture optimized for real-time performance. The workflow includes:
-
Voice Capture: The browser captures microphone input from the user.
-
Audio Streaming: Audio is streamed to the backend via WebSocket in real-time.
-
Speech-to-Text: The backend uses
RealtimeSTT(based onfaster_whisper) to transcribe speech to text. -
AI Response Generation: The transcribed text is sent to a language model (e.g., GPT) to generate a response.
-
Text-to-Speech: The AI’s response is converted into audio using
RealtimeTTS. -
Audio Playback: The synthesized voice is played back to the user via the browser, completing the loop.
Project Link
👉 GitHub Repository:
https://github.com/KoljaB/RealtimeVoiceChat
Use Cases
-
Virtual Assistants: Build interactive voice-controlled AI assistants.
-
Customer Service: Implement AI voice agents for real-time customer support.
-
Language Learning: Develop speaking practice tools for language learners.
-
Accessibility Tools: Provide voice-based UIs for visually impaired or mobility-limited users.
-
Interactive Entertainment: Enhance games or VR experiences with voice-enabled NPCs and systems.
Related Posts