Audio-SDS – An extended text-conditioned audio diffusion model introduced by NVIDIA
What is Audio-SDS?
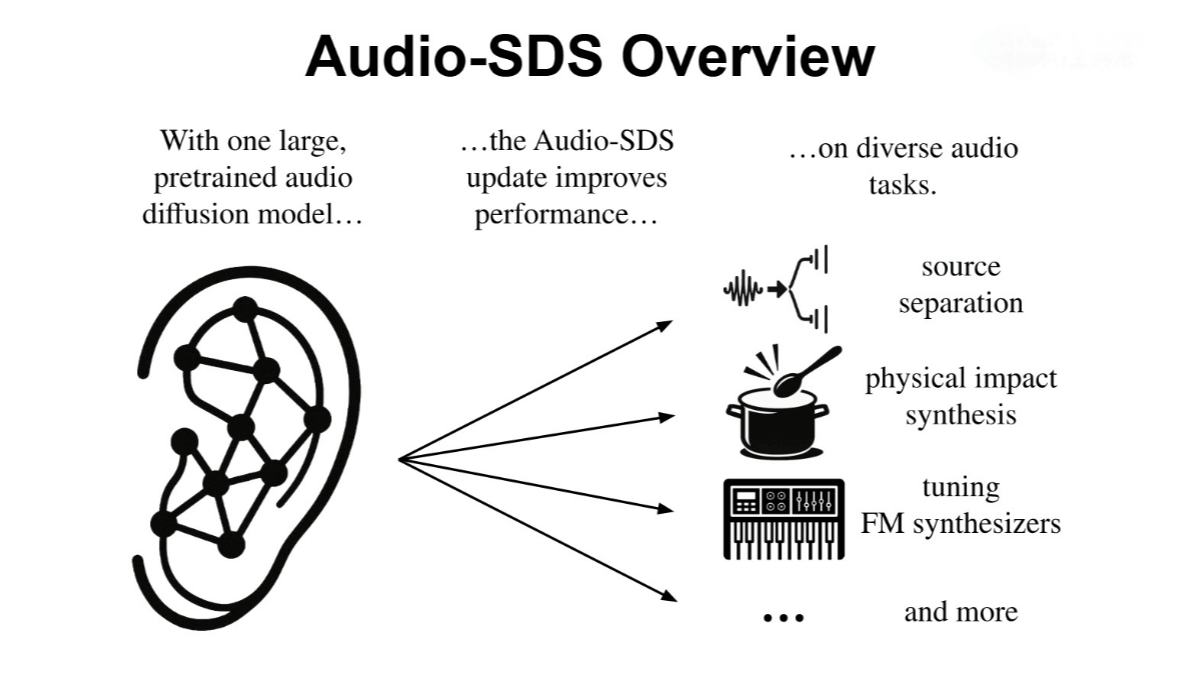
Audio-SDS is an innovative technology developed by NVIDIA’s AI research team that extends Score Distillation Sampling (SDS) to text-conditioned audio diffusion models, marking a significant breakthrough in the field of audio processing. Without requiring retraining, it can transform any pretrained audio diffusion model into a versatile tool for sound generation, source separation, FM synthesis, speech enhancement, and more. Audio-SDS allows highly customizable audio generation guided by text prompts, making it suitable for both creative and industrial applications.
Key Features of Audio-SDS
-
Sound Effect Generation: Generates various ambient or creative sound effects from text prompts, such as explosions or wind sounds—ideal for game development and virtual reality (VR) applications.
-
Source Separation: Accurately extracts target audio tracks from mixed audio, useful in music production and video post-processing. For example, it can separate audio sources in real-world recordings without manual annotations or specialized datasets.
-
Physical-Audio Simulation: Models how physical interactions (e.g., object collisions) affect sound output.
-
FM Synthesis Parameter Tuning: Supports high-quality frequency modulation synthesis for expressive timbre design.
-
Speech Enhancement: Improves speech clarity, making it suitable for use in audio editing software and smart voice assistants.
Technical Principles of Audio-SDS
-
Pretrained Audio Diffusion Models: Audio-SDS builds upon existing pretrained diffusion models that can generate high-quality audio samples and contain rich audio priors.
-
Text-Conditioned Guidance: Uses text prompts encoded into conditional vectors to guide the audio generation process, ensuring outputs align with textual descriptions.
-
Score Distillation Sampling (SDS):
-
Noise Injection: Adds random noise to audio samples to simulate noisy audio.
-
Loss Computation: Measures the difference between the noisy and target audio samples, optimizing the model via gradient descent to minimize the predicted-versus-actual noise gap.
-
Optimization Target: SDS minimizes the KL divergence between the noise distribution and the true distribution based on the diffusion model’s probability density.
-
-
Multifunctional Adaptability: Without retraining, Audio-SDS repurposes pretrained audio diffusion models for a variety of tasks, such as sound generation, source separation, FM synthesis, and speech enhancement.
-
Efficient Inference: The optimized SDS algorithm delivers high-quality results with reduced computational complexity, improving its viability for real-time applications.
Project Resources for Audio-SDS
-
Project Page: https://research.nvidia.com/labs/toronto-ai/Audio-SDS/
-
arXiv Paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2505.04621
Application Scenarios of Audio-SDS
-
Sound Effect Generation: Create realistic ambient or creative sound effects—like explosions, wind, or rain—based on text prompts. Ideal for immersive audio design in films, games, and VR applications.
-
Source Separation: Extract target audio elements from complex sound mixtures, such as isolating vocals from background music, aiding producers in mixing or generating new tracks.
-
Audio Editing: Provide content creators and music producers with efficient tools that lower the barrier to professional audio editing—generate high-quality sound using simple text inputs without needing advanced skills.
-
Music Education: Isolate acapella tracks to create karaoke versions or support music transcription and learning tasks.
-
Smart Homes: Automatically detect household sounds such as baby cries or leaking faucets, enhancing smart home awareness and automation.
Related Posts