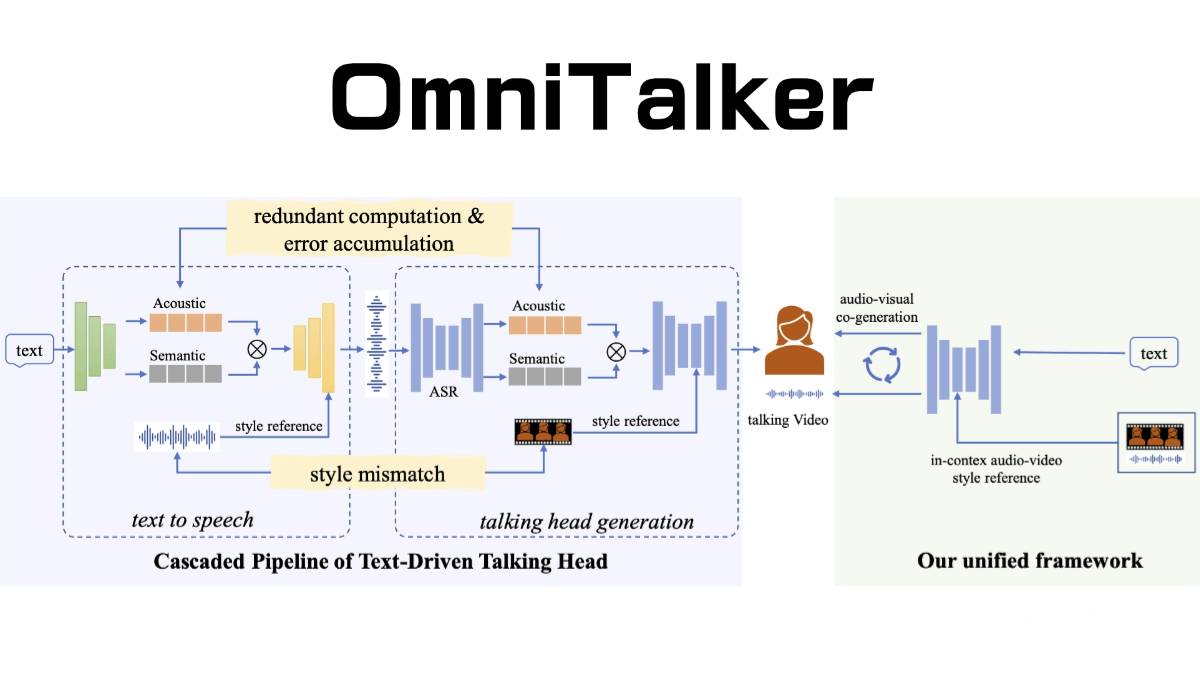
What is DeepScientist?
DeepScientist is an autonomous research system developed by Westlake University and other institutions, enabling full-process automation from hypothesis generation to experimental validation, result analysis, and paper writing. Through a multi-agent architecture and reinforcement learning strategies, the AI can continuously explore, verify, and advance scientific frontiers without human intervention. The system is built around a closed-loop “Hypothesize–Verify–Analyze” process, combined with Bayesian optimization, treating scientific discovery as a problem of finding optimal solutions in a vast methodological space. DeepScientist also features a Findings Memory, which records and reuses historical experimental results to enhance research efficiency and innovation.

Key Features of DeepScientist
-
Automated Hypothesis Generation: The system can autonomously propose new research hypotheses or improvements based on existing knowledge and experimental results, enabling automated innovation.
-
Experiment Design and Execution: It converts hypotheses into executable experimental workflows or code, automatically builds experimental environments, runs models, collects data, and validates results.
-
Result Analysis and Report Generation: After experiments, the system automatically analyzes results, summarizes patterns, and generates academic reports or draft papers, supporting direct research output.
-
Findings Memory Management: Records all experiments, hypotheses, and results to form a reusable knowledge base, assisting future research decisions.
-
Autonomous Optimization and Learning: Uses Bayesian optimization and other methods to balance exploration and exploitation in research, continuously improving efficiency and outcomes.
-
Multi-Agent Collaboration: Multiple specialized AI agents (for hypothesis generation, code execution, result analysis, etc.) work collaboratively to create a safe, controllable, and modular research workflow.
-
Safety and Verification Mechanisms: Uses sandboxed and containerized execution strategies to ensure experiment safety, result reliability, and automatic verification of conclusions.
Technical Principles of DeepScientist
-
Scientific Discovery as an Optimization Problem: Treats research innovation as finding optimal solutions in a vast methodological space, using Bayesian optimization and surrogate models to efficiently evaluate and filter hypotheses.
-
Closed-Loop Research Process: A “Hypothesize–Verify–Analyze” three-stage cycle continuously generates, tests, and refines scientific hypotheses, forming a self-driven research iteration system.
-
Multi-Agent Architecture: Composed of specialized agents responsible for strategy planning, code implementation, result analysis, and report generation, collaboratively completing the full research workflow.
-
Findings Memory System: Maintains a long-term knowledge repository storing past experiments, hypotheses, and results to guide new research exploration and optimization.
-
Hierarchical Verification and Surrogate Evaluation: Uses a two-tier validation strategy (low-fidelity and high-fidelity) where surrogate models first assess potential before running computationally intensive real experiments, saving resources.
-
Containerized and Sandboxed Execution Environment: Runs code and experiments in isolated, secure environments to prevent conflicts and errors, ensuring reproducibility and trustworthy results.
-
Automated Result Re-Validation: The system independently re-executes verification after experiments to prevent false positives and ensure the reliability and verifiability of scientific conclusions.
Project Links
-
Official Website: https://ai-researcher.net
-
GitHub Repository: https://github.com/ResearAI/DeepScientist
-
arXiv Technical Paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2509.26603
Application Scenarios of DeepScientist
-
AI Algorithm Research: Can autonomously explore model architectures, optimization strategies, and training methods, advancing AI reasoning efficiency, interpretability, and robustness.
-
Automated Scientific Innovation: Automatically generates and validates new hypotheses in fields like machine learning, computer vision, and natural language processing, accelerating research iteration.
-
Experimental Science Assistance: Applicable to disciplines like physics, chemistry, and biology that require extensive experimental validation, automatically screening potential discoveries through virtual experiments and data analysis.
-
Agent System Optimization: Improves strategies and communication mechanisms in multi-agent collaboration or reinforcement learning tasks, optimizing system performance.
-
Research Workflow Automation: Helps research teams automate the entire process from conception to report generation, enhancing efficiency and output quality.
-
Academic Paper Generation and Peer Review Simulation: Automatically drafts papers based on experimental results and performs self-checks and quality evaluation using AI review modules.