Kimi Linear – A New Hybrid Linear Attention Architecture Open-Sourced by Moonshot AI
What is Kimi Linear?
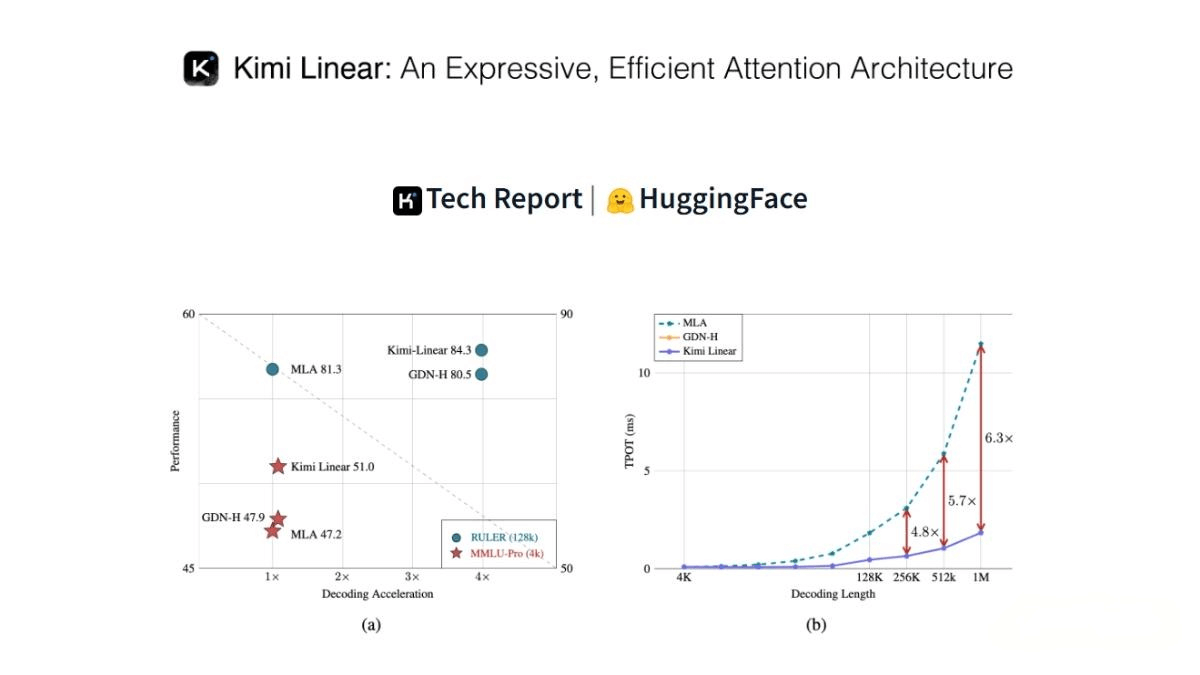
Kimi Linear is a new hybrid linear attention architecture developed by Moonshot AI (月之暗面), designed to enhance the efficiency and performance of large language models (LLMs) in long-sequence tasks. Its core component, Kimi Delta Attention (KDA), introduces a refined channel-level gating mechanism and a highly efficient block processing algorithm, significantly improving both expressive power and hardware efficiency. Kimi Linear adopts a 3:1 hybrid design combining KDA and full attention layers (MLA), reducing KV cache usage by 75% and achieving a 6.3× decoding speedup when processing million-token sequences. The Kimi Linear architecture outperforms traditional full attention mechanisms on both short and long-sequence tasks and demonstrates excellent performance in reinforcement learning scenarios.
Main Features of Kimi Linear
-
Efficient Long-Sequence Processing:
Through its hybrid linear attention architecture, Kimi Linear reduces KV cache usage by 75%, achieving a 6.3× throughput improvement in 1M-token decoding tasks. -
Precise Information Management:
The Kimi Delta Attention (KDA) module employs a channel-level gating mechanism that enables the model to selectively retain key information and forget irrelevant content, strengthening its long-sequence handling capability. -
Enhanced Reasoning Ability:
Kimi Linear excels in reinforcement learning tasks requiring complex reasoning, achieving faster training accuracy growth and outperforming full attention models on test sets. -
Hardware-Friendly Design:
With an efficient block processing algorithm, Kimi Linear fully leverages modern GPUs’ Tensor Cores, achieving high matrix multiplication throughput while reducing computation time and resource consumption. -
Adaptable Across Tasks:
Kimi Linear performs strongly on both short and long-sequence tasks, making it suitable for applications such as language understanding, code generation, and mathematical reasoning, with excellent generalization capability.
Technical Principles of Kimi Linear
-
Hybrid Linear Attention Architecture:
Kimi Linear is built on a 3:1 hybrid design, inserting one full attention (MLA) layer after every three Kimi Delta Attention (KDA) layers. This design combines the efficiency of linear attention with the expressive strength of full attention while reducing KV cache usage and boosting decoding speed. -
Kimi Delta Attention (KDA):
The core module of Kimi Linear achieves efficient processing through:-
Fine-Grained Gating Mechanism:
Introduces channel-level gating where each feature dimension has an independent forget rate, enhancing positional awareness similar to RoPE positional encoding. -
Hardware-Efficient Block Processing Algorithm:
Uses block-parallel computation to reduce computational load and improve hardware utilization. KDA’s state transition can be viewed as a special diagonal plus low-rank (DPLR) matrix, which reduces computational complexity through structured constraints. -
No Positional Encoding (NoPE):
The MLA layers in Kimi Linear omit explicit positional encodings (e.g., RoPE), delegating positional information entirely to the KDA layers. This simplification enhances robustness and extrapolation in long-text tasks. -
Integration with Mixture-of-Experts (MoE):
Kimi Linear combines with MoE technology, expanding parameter scale through sparse activation. The total model has 48 billion parameters, with only 3 billion activated per forward pass, improving training and inference efficiency.
-
Project Links
-
Hugging Face Model Hub: https://huggingface.co/moonshotai/Kimi-Linear-48B-A3B-Instruct
-
Technical Paper: https://github.com/MoonshotAI/Kimi-Linear/blob/master/tech_report.pdf
Application Scenarios of Kimi Linear
-
Long-Text Generation:
Excels in handling million-token sequences with a 6.3× decoding speedup, ideal for generating long novels, research reports, and other extended texts. -
Code Generation and Understanding:
With strong long-sequence processing capabilities, Kimi Linear performs exceptionally well in code generation and comprehension, supporting complex logic and long code snippets. -
Mathematical Reasoning and Problem Solving:
In reinforcement learning for math tasks, Kimi Linear achieves faster training accuracy improvement and better test performance than full attention models, making it well-suited for complex mathematical problems. -
Language Understanding and Question Answering:
Performs effectively on both short and long-sequence language understanding and QA tasks, enabling deeper contextual comprehension and generation. -
Multimodal Tasks:
Applicable to multimodal scenarios such as image captioning and video content understanding, supporting longer text descriptions and more complex reasoning chains.
Related Posts