What is Lego-Edit?
Lego-Edit is an open-source instruction-based image editing framework developed by Xiaomi. It leverages the generalization ability of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to perform flexible image editing. Built as a model-level toolkit, it integrates multiple efficiently trained models capable of diverse image operations.
Lego-Edit is trained through a three-stage progressive reinforcement learning strategy: starting with supervised fine-tuning (SFT), followed by reinforcement learning (RL) on specific tasks, and finally large-scale RL training with massive unannotated instructions to enhance its ability to handle flexible instructions.
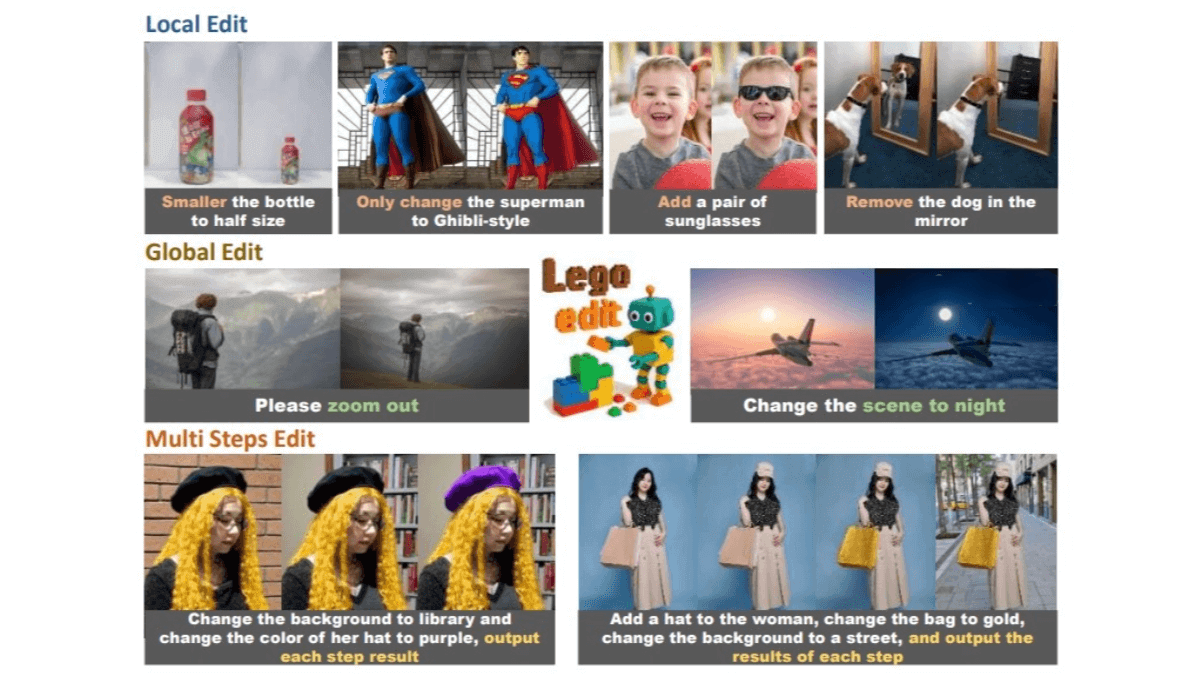
Its main advantages include strong generalization, achieving state-of-the-art performance across benchmarks, support for local, global, and multi-step editing, and mask input for precise region control. Moreover, Lego-Edit can integrate new tools without retraining, making it highly extensible.
Key Features of Lego-Edit
-
Powerful Image Editing: Handles a wide range of editing tasks based on user instructions, including local edits, global edits, and multi-step operations, suitable for diverse scenarios.
-
Flexible Instruction Understanding: Powered by MLLMs, Lego-Edit can interpret and execute open-domain instructions—even unseen ones—through strong reasoning capabilities.
-
Model-Level Toolkit Utilization: Includes multiple efficiently trained models for specific image operations. The MLLM coordinates these models to execute fine-grained editing tasks with high accuracy.
-
Seamless Tool Integration: New editing tools can be integrated without additional fine-tuning, enabling quick adaptation to evolving editing needs.
-
Mask Input for Precision: Supports mask-based editing, allowing users to precisely define target areas for modification while leaving other regions untouched.
-
Open Source & Easy to Use: Code is released under the Apache 2.0 license, and models under CC BY-NC 4.0. With simple environment setup and pretrained model downloads, users can start editing images via a Gradio WebUI, lowering the entry barrier.
Technical Principles of Lego-Edit
-
Model-Level Toolkit: Combines multiple models, each optimized for a specific image operation (e.g., color adjustment, object replacement), providing a versatile editing toolbox.
-
MLLM-Driven Orchestration: The MLLM interprets instructions and coordinates different models in the toolkit, transforming instructions into precise editing operations.
-
Three-Stage Progressive RL Training:
-
SFT – Supervised fine-tuning for basic editing knowledge.
-
RL – Reinforcement learning on specific tasks to build reasoning and tool-usage skills.
-
Large-Scale RL with Unlabeled Instructions – Using feedback from large critic models to improve flexibility in handling diverse commands.
-
-
Mask Input Mechanism: Enables precise region-based editing for greater accuracy and control.
-
Tool Integration Without Retraining: Easily incorporates new tools to expand functionality while maintaining efficiency and scalability.
Project Links
-
Official Website: https://xiaomi-research.github.io/lego-edit/
-
GitHub Repository: https://github.com/xiaomi-research/lego-edit
-
arXiv Paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2509.12883
Application Scenarios
-
Creative Design: Designers can quickly realize creative ideas through simple instructions, enabling complex image composition, style transfer, and more—boosting efficiency and inspiration.
-
Content Creation & Editing: In video production, advertising, or social media, creators can easily adjust colors, replace backgrounds, and add effects to enhance visual content.
-
E-commerce & Product Display: Online sellers can optimize product images by removing flaws, adjusting lighting, or adding virtual scenes to improve presentation and boost sales.
-
Education & Training: Teachers can create visual teaching materials, while students learn editing skills, fostering creativity and visual literacy.
-
Personal Photo Enhancement: Everyday users can beautify photos—removing backgrounds, adjusting skin tones, or adding decorative elements—for social sharing or personal collections.
-
VR & Game Development: Developers can generate and edit in-game assets, such as character appearances or scene elements, improving efficiency and enriching visuals.
Related Posts